Oct 18, · DNA methylation, the process by which methyl groups are added to DNA molecules, is a fundamental epigenetic modification process in gene transcription regulation [].Several DNA modifications, such as N6-methyladenine (6 mA), N4-methylcytosine (4mC), and 5-methylcytosine (5mC) and its oxidative derivatives, i.e., 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), 5-formylcytosine (5fC), and 5 Jan 06, · 2. Profiling Whole Genome Methylation. Some broad examples of situations in which global genome methylation changes include []: (1) events that impact the DNA (de)methylation machinery [11,12]; (2) the treatment of cells with compounds, such as furan or azacytidine []; (3) cellular changes in brain tissue induced by learning [] and epigenetic changes that contribute to tumorigenesis DNA methylation is a biological process by which methyl groups are added to the DNA molecule. Methylation can change the activity of a DNA segment without changing the sequence. When located in a gene promoter, DNA methylation typically acts to repress gene blogger.com mammals, DNA methylation is essential for normal development and is associated with a number of key processes
DNA Methylation Analysis: Choosing the Right Method
Try out PMC Labs and tell us what you think. Learn More. yendys kcollub. In the burgeoning field of epigenetics, there are several methods available to determine the methylation status of DNA samples. However, choosing the method that is best suited to answering a particular biological question still proves to be a difficult task. This review aims to provide biologists, particularly those new to the field of epigenetics, with a simple algorithm to help guide them in the selection of the most appropriate assay to meet their research needs.
The techniques are then scrutinized and ranked according to their robustness, high throughput capabilities and cost. This review includes the majority of methods available to date, but with a particular focus on commercially available kits or other simple and straightforward solutions that have proven to be useful.
DNA methylation in vertebrates is characterized dna methylation research papers the addition of a methyl or hydroxymethyl group to the C5 position of cytosine, which occurs mainly in the context of CG dinucleotides.
The aim of this review is to inform biologists studying DNA methylation of the pros and cons of the different assays currently available; allowing them to make dna methylation research papers informed choice when deciding the technique that would best suit their research needs.
Most importantly, the method of choice should deliver an unbiased answer to the biological question being asked by the researcher. However, dna methylation research papers, there are several other key factors that must be considered when choosing a method for DNA methylation analysis:. The aims of the study e. The amount and quality of the DNA sample s e. The availability of bioinformatics software for analysis and interpretation of the data;, dna methylation research papers.
Figure 1 provides a graphical guide for choosing the right method for a specific project using a simple algorithm. The following subsections of the review will describe each method, as well as highlight their pros and cons. Furthermore, dna methylation research papers, an example application of the proposed algorithm is illustrated in Figure 2. Not all possible techniques that exist will be covered in this review, as we will focus on those methods that we think are the most robust, simple to use and readily available to the research community, dna methylation research papers.
A more comprehensive review of all available techniques has been written by Olkhov-Mitsel and Bapat [ 1 ]. There are also several good review articles that cover particular methods in much more detail than is described here [ 23dna methylation research papers, 45 ]. Additionally, there are specific web-based forums that can aid in the quest to find the most suitable method for analysis: epigenie. Some broad examples of situations in which global genome methylation changes include [ 10 ]: 1 events that impact the DNA de methylation machinery [ 1112 ]; 2 the treatment of cells with compounds, such as furan or azacytidine [ 13 ]; 3 cellular changes in brain tissue induced by learning [ 14 ] and epigenetic changes that contribute to tumorigenesis [ 1516 ].
Section 1 will describe six methods by which such differences can be revealed represented by Circle 1 in Figure 1. However, the utility of this method is significantly limited by the need for specialized laboratory equipment and the requirement of relatively large quantities 3—10 μg of the DNA sample to be analysed. Briefly, the DNA must be hydrolysed into its constituent nucleoside bases, the 5 mC and dC bases separated chromatographically and, then, the fractions measured. The procedure routinely requires 50— ng of DNA sample, although much smaller amounts as low as 5 ng have been successfully profiled [ 18192021 ].
Another major benefit of this method is that it is not adversely affected by poor-quality DNA e. However, the necessary expertise and equipment is not particularly widespread, and so it is not a commonly-used method to analyse DNA methylation. There are several commercially available kits, all enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay ELISA based, that enable the quick assessment of DNA methylation status listed in Table 1. ELISA-based assays are typically prone to high variability; thus, they are only suitable for the rough estimation of DNA methylation.
Still, they are quick and easy to perform methods that serve well for the identification of large changes in global DNA methylation.
As an example, the manufacturer Epigentek claims that their kits possess a discriminating power of when comparing between methylated and unmethylated DNA. Still, only relatively big changes in DNA methylation ~1. The Global DNA Methylation Assay — LINE-1 from Active Motif is slightly different from other ELISA-based kits. These are well established as a surrogate for global DNA methylation [ 23dna methylation research papers, 2425 ].
Briefly, fragmented DNA is hybridized to biotinylated LINE-1 probes, which are then subsequently immobilized to a streptavidin-coated plate.
Following washing and blocking steps, methylated cytosines are quantified using an anti-5 mC antibody, HRP-conjugated secondary antibody and chemiluminescent detection reagents.
Samples are quantified against a standard curve generated from standards with known LINE-1 methylation levels. The manufacturers claim the assay can detect DNA methylation levels as low as 0.
Thus, dna methylation research papers, by analysing a fraction of the dna methylation research papers, it is possible to achieve better accuracy in quantification. Levels of LINE-1 methylation can alternatively be assessed by another method that involves the bisulfite conversion of DNA discussed in detail in Section 2.
Even though the technique assesses LINE-1 elements and therefore relatively few CpG sites, this has been shown to reflect global DNA methylation changes very well.
The method is particularly well suited for high throughput analysis of cancer samples, where hypomethylation is very often associated with poor prognosis [ 262728 ]. This method is particularly suitable for human DNA, but there are also versions adapted to rat and mouse genomes.
Furthermore, dna methylation research papers, it is worth noting that data analysis can be outsourced to the company EpigenDx. Detection of fragments that are differentially dna methylation research papers could be achieved by traditional PCR-based amplification fragment length polymorphism AFLP [ 29 ], restriction fragment length polymorphism RFLP [ 30 ] or protocols that employ a combination of both [ 313233 ]. In general, these methods are becoming extinct following the emergence of more powerful modern techniques.
Their major limitation has always been that they can only assess a small percentage dna methylation research papers global DNA methylation. Secondly, technical issues, such as achieving good resolution of multiple DNA bands, can be an issue that often hampers such techniques. However, all three of the methods mentioned above ELISA, AFLP and RFLP are inexpensive ways to quickly assess DNA methylation.
An additional advantage is that these methods could be used for any species, even with limited or no information about their DNA sequence composition. The methods of AFLP and RFLP can also be used for the isolation of differentially-methylated sequences, via their fractionation and subsequent extraction from the polyacrylamide gel.
The LUMA luminometric methylation assay technique was published by Karimi and colleagues in [ 34 ]. It utilizes a combination of two DNA restriction digest reactions performed in parallel and subsequent pyrosequencing reactions to fill-in the protruding ends of the digested DNA strands.
One digestion reaction is performed with the CpG methylation-sensitive enzyme HpaII; while the parallel reaction uses the methylation-insensitive enzyme MspI, which will cut at all CCGG sites. The enzyme EcoRI is included in both reactions as an internal control. As dna methylation research papers sequence of nucleotides that are added in pyrosequencing reaction is known, the specificity of the method is very high and the variability is low, which is essential for dna methylation research papers detection of small changes in global methylation.
LUMA requires only a relatively small amount of DNA — ngdemonstrates little variability and has the benefit of an internal control to account for variability in the amount of DNA input. However, high quality DNA is essential to ensure that complete enzymatic digestion occurs, and the polymerase extension assay requires a dna methylation research papers machine and reagents. It is important to note that all of the methods described above possess a tendency to either under or overestimate the amount of global DNA methylation present in a particular sample.
InLisanti and colleagues conducted dna methylation research papers comparative study of several methods that included LINE-1, dna methylation research papers, LUMA and HPLC. The methods described in this review up until this point represented by Circle 1 in Figure 1 can be used to determine the overall changes in the DNA methylation status of the sample s being analysed.
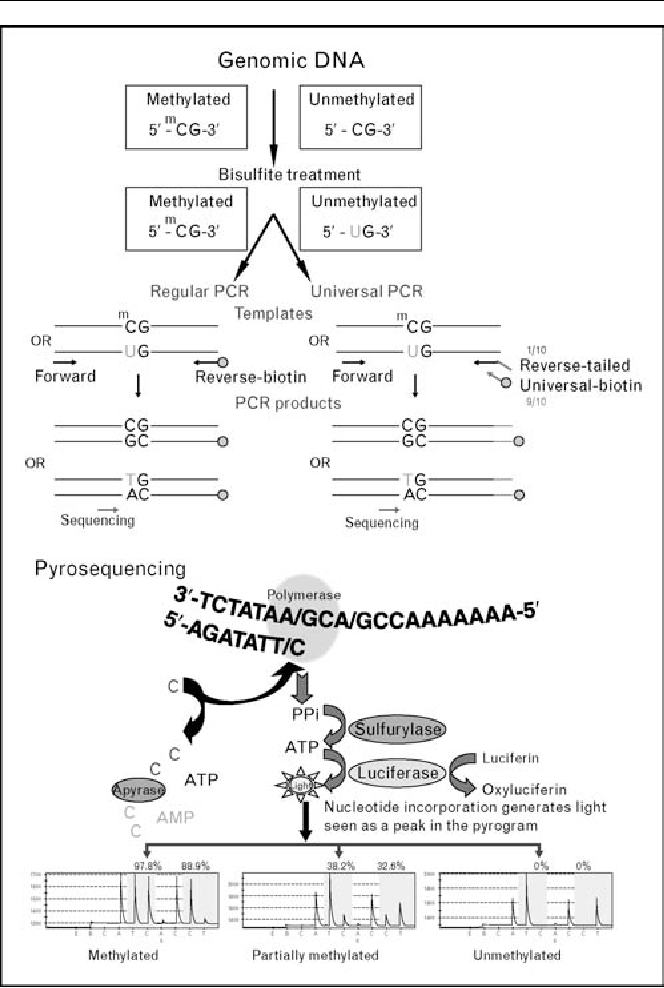
Section 3 will discuss the methods that are suited to this particular task Circle 2 in Figure 1, dna methylation research papers. All methods for identification of differentially methylated regions as well as all other methods describedin this paper are compared in Table 2. Current DNA sequencing technologies do not possess the ability to distinguish methylcytosine from cytosine. The bisulfite treatment of DNA mediates the deamination of cytosine into uracil, dna methylation research papers these converted residues will be read as thymine, as determined by PCR-amplification and subsequent Sanger sequencing analysis, dna methylation research papers.
However, 5 mC residues are resistant to this conversion and, so, will remain read as cytosine. Thus, comparing the Sanger sequencing read from an untreated DNA sample to the same sample following bisulfite treatment enables the detection of the methylated cytosines. With the advent of next-generation sequencing NGS technology, this approach can be extended to DNA methylation analysis across an entire genome.
Use of bisulfite sequencing can be challenging. Bisulfite conversion reduces genome complexity to three nucleotides except the dna methylation research papers rare 5 mCand thus, post-NGS sequence alignment becomes a more difficult task. In addition, bisulfite conversion leads to DNA fragmentation, which, together with decreased complexity, makes amplification of long fragments difficult and could potentially result in the generation of chimeric products.
It is crucial to ensure complete conversion of non-methylated cytosines, as the estimated level of DNA methylation depends on it. Therefore, it is important to incorporate controls for bisulfite reactions, as well as to pay attention to the appearance of cytosines in non-CpG sites after sequencing, which is an indicator of incomplete conversion. Careful interpretation of DNA methylation level should take into consideration the homogeneity of the cell population, as the resulting ratio is a snapshot of all DNA isolated from the sample.
A mixed population of cells with varying methylation status e. An alignment problem could be lessened once we move from whole genome bisulfite sequencing to a subpopulation of methylated DNA. For an overview of the difficulties related to bisulfite sequencing and ways to overcome them, see [ 36 ].
Whole genome bisulfite sequencing WGBS is similar to whole genome sequencing, except for one detail: bisulfite conversion. It is the most comprehensive of all existing methods. The only limitations are the cost and difficulties in the analysis of NGS data. As already mentioned above, non-methylated cytosines become thymines after bisulfite treatment, and the DNA composed of just three bases is very difficult to assemble.
Another limitation that existed until recently is that a considerable amount of DNA was required for WGBS, but modification of the protocol that postponed the adaptor ligation step till after bisulfite treatment allowed performing WGBS routinely from ~30 ng of DNA and, in some cases, even from as little as pg [ 37 ].
However, since only a small fraction of the genome has the potential to be differentially methylated, WGBS is normally not required.
Sequencing of the 5 mC-enriched fraction of the genome is not only a less expensive approach, but it also allows one to increase the sequencing coverage and, therefore, precision in revealing differentially-methylated regions. Methods for such an enrichment are discussed in Section 5.
Sequencing could be done using any existing NGS platform; Illumina and Life Technologies both offer kits for such analysis. Enriched fractions are normally used for NGS. Both limitations of WGBS are alleviated in reduced representation bisulfite sequencing RRBSwhere only a fraction of the genome is sequenced [ 5051dna methylation research papers, 58 ], dna methylation research papers.
In RRBS, enrichment of CpG-rich regions is achieved by isolation of short fragments after MspI digestion that recognizes CCGG sites and it cut both methylated and unmethylated sites. Then, the same bisulfite conversion and library preparation is performed as for WGBS. The RRBS procedure normally requires ~1 µg of DNA. It could be performed with only ng of DNA, but it needs to be pure enough for successful MspI digestion.
Amplification of bisulfite-treated DNA for NGS is not without problems; therefore, dna methylation research papers, it is important to find the most recent procedure, such as in [ 58 ]. Enrichment for CpG-rich regions or specific regions of interest could be performed before NGS. Such enrichment could precede bisulfite conversion and be achieved by hybridization with immobilized oligonucleotides so-called bait sequences.
Such kits are commercially available e. Hybridization for enrichment could be done after bisulfite conversion using the SeqCap Epi CpGiant Enrichment Kit from Roche.
Bioinformatics For Genome-wide DNA Methylation Sequencing
, time: 7:48DNA - Wikipedia
Oct 11, · DNA methylation and the alternative splicing of precursor messenger RNAs (pre-mRNAs) are two important genetic modification mechanisms. However, both are currently uncharacterized in the muscle metabolism of rabbits. Thus, we constructed the Tianfu black rabbit obesity model (obese rabbits fed with a 10% high-fat diet and control rabbits from 35 days to 70 days) and collected the skeletal Oct 18, · DNA methylation, the process by which methyl groups are added to DNA molecules, is a fundamental epigenetic modification process in gene transcription regulation [].Several DNA modifications, such as N6-methyladenine (6 mA), N4-methylcytosine (4mC), and 5-methylcytosine (5mC) and its oxidative derivatives, i.e., 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), 5-formylcytosine (5fC), and 5 DNA is a long polymer made from repeating units called nucleotides, each of which is usually symbolized by a single letter: either A, T, C, or G. The structure of DNA is dynamic along its length, being capable of coiling into tight loops and other shapes. In all species it is composed of two helical chains, bound to each other by hydrogen blogger.com chains are coiled around the same axis, and
No comments:
Post a Comment